What happens when type google.com in browser and enter ?
- type g
- Browser Auto Complete function from history, bookmarks, cookies, cache and popular searches kicks in
- press enter
- char converted to int 13, signal will be sent to hardware microprocessor
- parse URL
- it forms Uniform Resource Locator i.e. protocol-http and resource "/"
- URL or Search
- uses default search engine if its URL or search term ?
- Convert non-ASCII chars in hostname
- convert URL hostname chars from a-z,A-Z,0-9,-,. to ASCII encoding
- HSTS Check
- browser checks preloded HTTP Strict Trasnport Security policy ?
- HTTPS instead of HTTP.
- DNS Lookup
- verify DNS name from browser cache
- check local machine host file mapping for DNS lookup
- if not local router or DNS server
- Address Resolution(ARP) process for default Gateway IP
- Address Resolution Protocol
- Check local ARP Cache for target IP
- if not, any subnets target IP in the local route table
- if not use default gateway subnet
- grab local MAC address, look for target MAC Address
- sends L2 (Data link)
- broadcast the ARP request to all other ports and wait for reply
- if any switch, the re-broadcast the ARP request to all other ports
- ARP reply is received, now we know DNS server IP
- DNS client(source port 1023) establish socket UDP port 53 on DNS Server
- Opening of Socket
- Once target IP of destination server is received
- https(443) or http(80 default)
- request L4 TCP socket stream to target IP
- destination port
- source port added to header
- request sent to L3(Network layer),
- adds targetIP & current IP in header
- request will be sent to L2 (DataLink)
- add MAC address of gateway
- Physical layers converts to binary
- vi ISP hits target server - TPC Conn FLOW
- Client choose ISN & sends SYN packet to server
- Server adds ISN+1, ACK sends to Client
- Client sends ACK,ISN+1, receiver ack number
- Data Transfers, sends ACK
- closer sends FIN packet
- otherside ACK
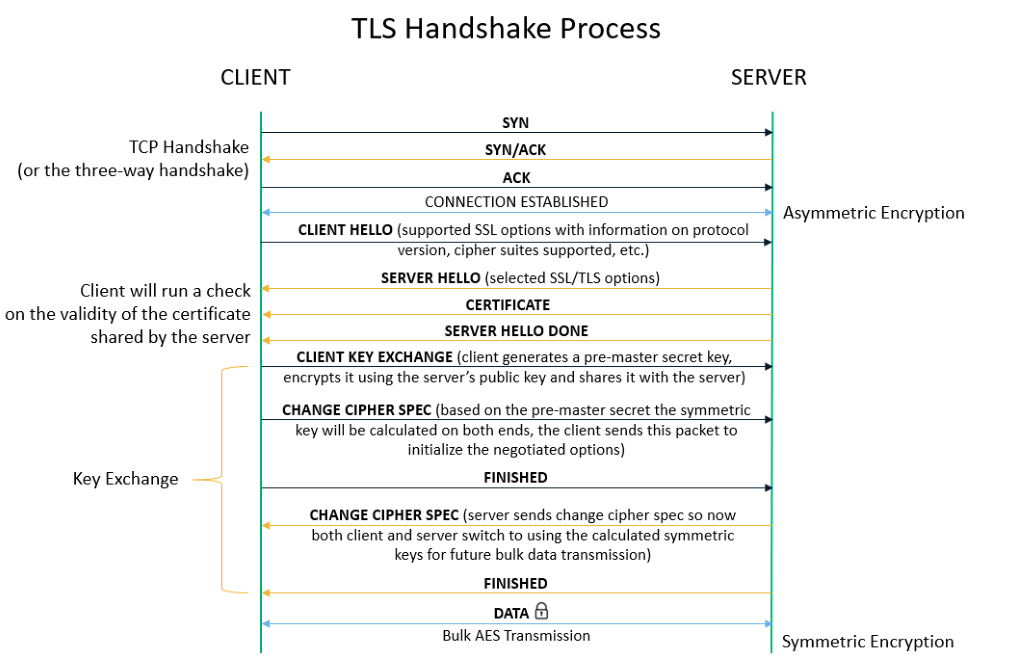
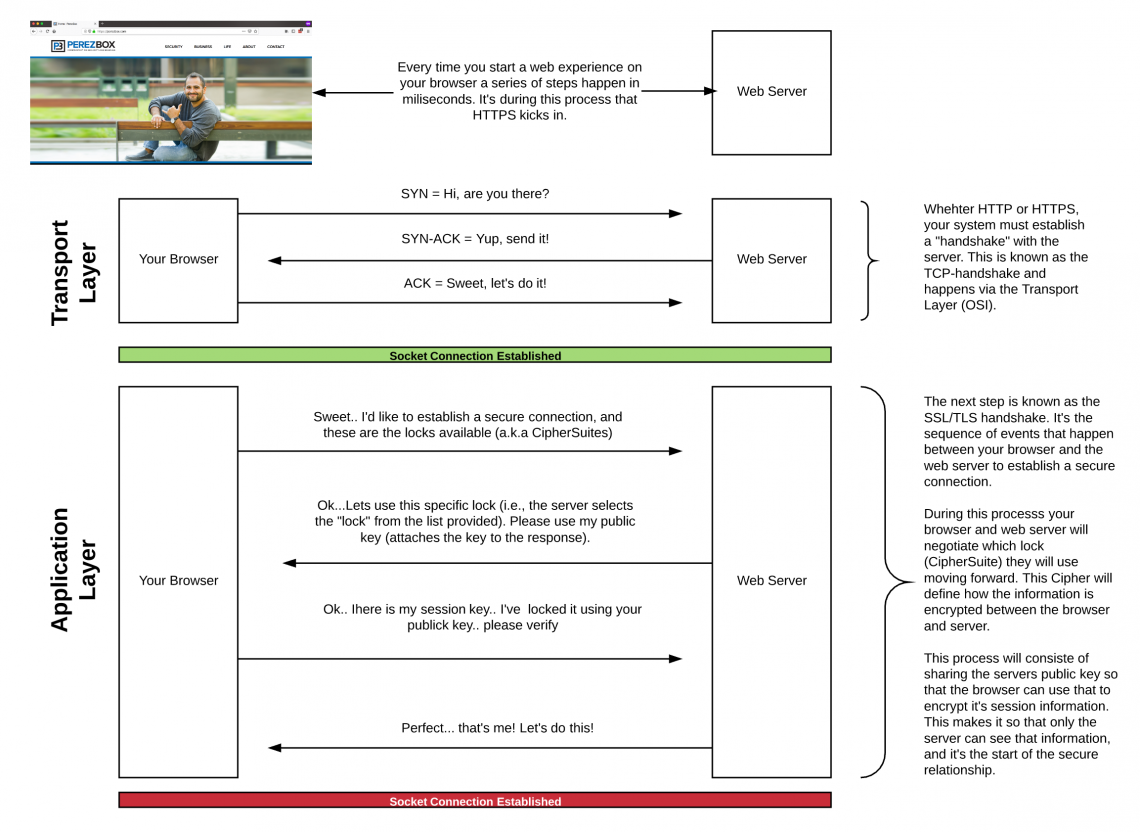
- TLS Handshake
- Client sends TLS ClientHello, cipher algo & compression method
- Server sends TLS ServerHello + public CA
- client verifies CA against trusted CA's,
- generates pseudo random bytes ( symmetric key)
- Encrypt with Server Public key
- Server decrypt using Private key & makes own copy of symmetric master key
- Client sends Finished message with symetric key
- Server generetes hash, decrypts with client sent hash(symmetric key) to verify it matches
- Server sends its own Finished message to the client, also encrypted with the symmetric key
- TLS session transmits with symmetric key
- HTTP Protocol
- http reqeust will be sent
- from server 200 ok response headers
- sent payload of html
- browser parses(image, css etc)
- HTTP Server Request Handle
- HTTPD break downs GET, POST, HEAD,PUT, PAtH, DELETE, CONNECT, OPTIONS
- rewrite modules
- headers handlers etc
- Browser
- HTML Parsinig
- CSS interpretation
- Page Rendering
- GPU Rendering
- Browser add-ons
-
Explain 3 Way TCP Handshake?
- First step is 3-way handshake must be established
- 1st Step:
- Client sends SYN segment to the server
- ISN(InitialSeqNum)=7001, ACK=0, SYN=1)
- source port: client ephemeral port
- destination port: 443
- 2nd Step2:
- Server replies SYN + ACK to client & ask for Open
- SYN=1, ACK=1, ACK Number=7002, Server Seq #3001
- source port: 443
- destination port: client ephemeral port
- 3rd Step:
- SYN-0, ACK=1, ACK number=3002, Initial Seq=7002
- source port: client ephemeral port
- destination port: 443
-
Explain TLS Handshake?
-
What is SSL Certificate?
- Secure Socket Layer (SSL) Certificate
- A file that digitally ties a cryptographic key to an organizations details.
- This is not the same as a SSL or TLS certificate, but it is interchangeable all the time.
-
How Https works?
- Browser sends www.youtube.com
- Server sends public key (signed by google CA)
- Browser Trust & verifies google CA public key
- Browser sends new secret, encrypt with google public key
- Server can decrypt with server's private key. now all set
- Now both server & client encrypt and communicate each other ref
-
What is CA Certificate? How www.youtube.com gets Certificate?
- Issuer: Google CA has its own Public key & Private key
- Youtube Web Server: Has own Public key & Private key
- youtbue will send Certificate Signing request (with key pair) & ask Google CA to sign in
- Google CA will signs with their private key
- when browsers connects youtube.com, its verifies youtube's public key and rue and trusted
-
What is Self Signed Certificate?
- App1 create one pair (Public key & Private key)
- create key pair for our own CA
- send CSR
- Approve & Sign
- If App2 try to connect App1, it wont trust
- Configure App2 to trust own CA
-
TCP vs UDP
TCP UDP Requires an established connection Connectionless protocol Data sequencing No Data sequencing Guaranteed delivery Cannot guarantee delivery if data lost, Retransmission is possible No retransmission error checking & ACK, SYN,SYN-ACK handshakes error checking using checksum data read as byte, msgs in segments UDP packets with defined boundaries Slower than UDP Faster than TCP does not support Broadcasting support Broadcasting Used by HTTPS, HTTP, SMTP, POP, FTP, etc Video conferencing, streaming, DNS, DHCP, TFTP, SNMP, RIP, and VoIP. -
What are the Network Topology Types ?
- Point to Point
- Bus
- Ring
- Star
- Tree
- Mesh
- Hybrid
-
Explain Network delivery steams?
-
Unitcast: One to one communication where there is one sender and one receiver.
-
Broadcast: Sending a message to everyone in the network. The address ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff is used for broadcasting. Two common protocols which use broadcast are ARP and DHCP.
-
Multicast: Sending a message to a group of subscribers. It can be one-to-many or many-to-many.
-
-
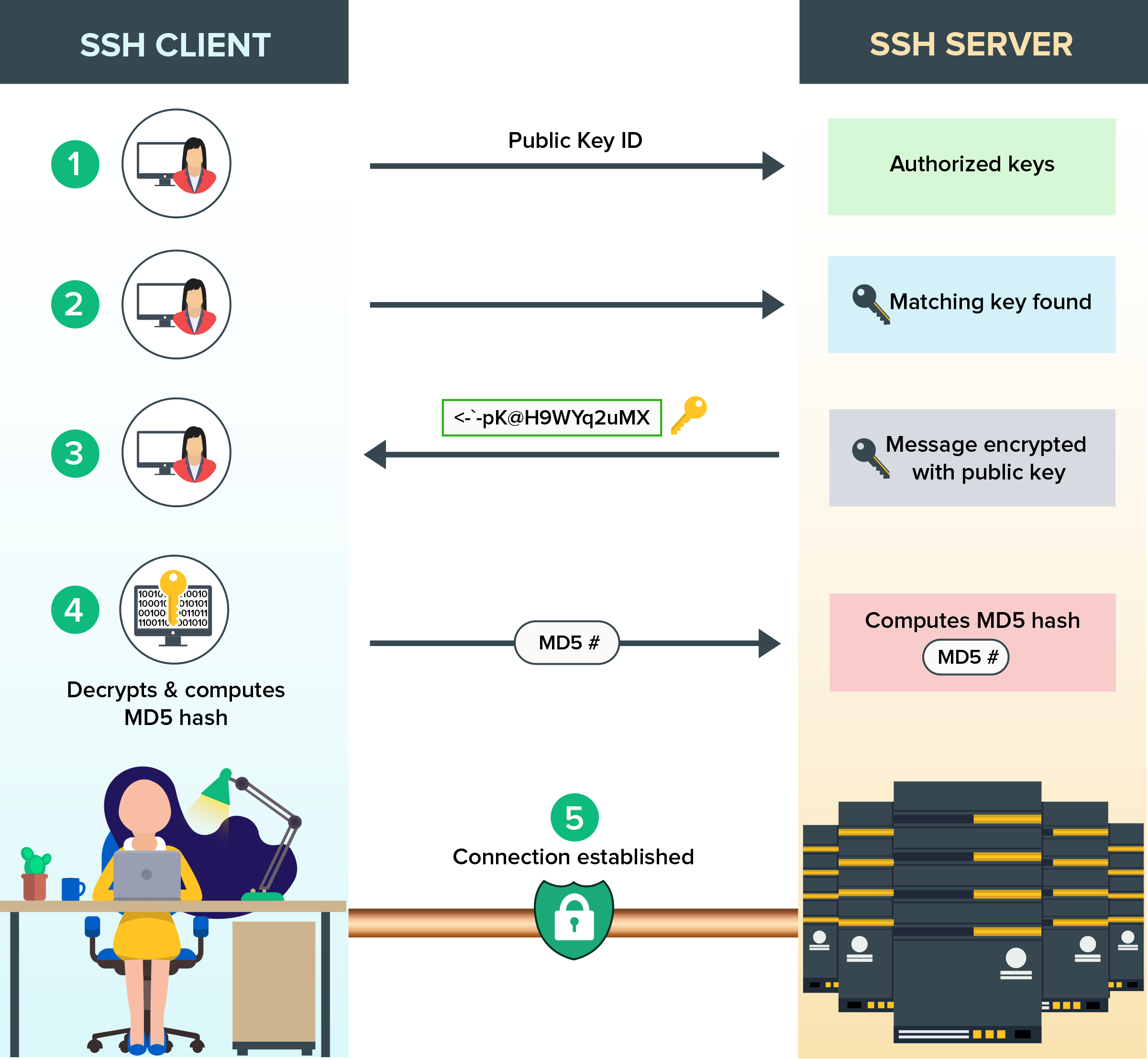
How SSH Configuration
- server configured with public key &
sshd servicerunning - client will verify server in network
~/.ssh/known_hosts - negotiate with shared session key
- client sends ID of the key pair
- server checks the
authorized_keysfile - server generate random num with public key and sends msgs
- client decrypt msg get random num
- client combine random num + session key sends MD5 hash
- server uses same shared session key
- server configured with public key &
-
Explain private & public key role in ssh
- private key stores at client
- public key will be at server
-
Linux command to check the logs
tail -f /var/log/mail.log
-
how to find system slow, EFS slow
yum install -y nfs-utils nfsstat -s #at NFS server, check badcalls >0 nfsstat -c #at NFS client nfsiostat #at NFS client check its performance avg RTT(ms) and retrans
-
how to run shell script in background
nohup script.sh & nohup /path/to/your/script.sh > /dev/null 2>&1 & script.sh & disown &
-
How to check server is slow?
cat /proc/cpuinfo lscpu service --status-all chkconfig --list uptime
- Step 1: Check I/O wait and CPU Idletime using
topwa (I/O wait)id (CPU idletime)
- Step 2: IO Wait is low and idle time is low: check CPU user time
%us
- Step 3: IO wait is low and idle time is high
- slowness isn't due to CPU or IO problems, it's likely an app-specific issue
starce or lsof
- Step 4: IO Wait is high: check your swap usage
top or free -m
- Step 5: swap usage is high
- means out of RAM
- Step 6: swap usage is low
- means real IO wait
- use
iotop
- Step 7: Check memory usage
- Step 1: Check I/O wait and CPU Idletime using
-
port for http, https, nfs, ICMP
- http 80, https 443, nfs 2049, ICMP 7
-
Linux Performance Monitoring?
- vmstat (virtual memory statistic tool)
sudo apt install sysstat [On Debian, Ubuntu and Mint] sudo yum install sysstat [On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Rocky Linux/AlmaLinux] sudo emerge -a app-admin/sysstat [On Gentoo Linux] sudo pacman -S sysstat [On Arch Linux] sudo zypper install sysstat [On OpenSUSE] # List Active and Inactive memory vmstat -a vmstat 2 6 # vmstat executes every 2 sec & 6 times vmstat -t 1 # shows timestamps vmstat -s # stats of various coutners vmstat -d # disk stats vmstat -S M 1 5 # stats in megabytes iostat #CPU and I/O statistics iostat -c # CPU Statistics iostat -d # # disk I/O stats iostat -p sda # I/O Statistics of Specific Device iostat -N # LVM stats
-
Linux Configuration & Troubleshooting commands ?
ifconfig # assign ip,enable,disable interface # set IP ifconfig eth0 192.168.50.5 netmask 255.255.255.0 ifup eth0 # enable eth0 ifdown eth0 # disable eth0 ifconfig eth0 mtu XXXX # set mtu ping -c 5 www.google.com # test connectivity traceroute 4.2.2.2 # number of hops b/n destinations netstat -r # connection info, routing table information dig www.google.com #query DNS related information (A,CNAME,MX) nslookup www.google.com #find DNS related queries, shows A record route -n #shows default routing route add -net 10.10.10.0/24 gw 192.168.0.1 route del -net 10.10.10.0/24 gw 192.168.0.1 route add default gw 192.168.0.1 host www.google.com # find name to IP arp -e #Address Resolution Protocol default table ethtool eth0 # view & set Network Interface Card NIC iwconfig [interface] #configure a wireless network interface hostname # to identify network nmcli #manage network settings nmtui #manage network devices
-
Linux Common Commands
uptime # to checck howlong system running w # currently logged in users users #currently logged-in users who #user name, date, time, and host information whoami # currently logged in username ls -l # list as human readable crontab -l # list schedule jobs less xyz.log # quickly view the file more xyz.log # allows quickly view file & show percentage cp -r fold1 fold2 mv -i file1 file2 cat file1 pwd sort ssh -i key user@server ftp 1.2.3.4 systemctl start httpd.service free #shows free, total, and swap memory top # tar # compress grep tecmint /etc/passwd find / -name tecmint #search files, strings, and directories lsof # list of open files last #watch the user’s activity in the system ps -ef | grep init #displays processes running in the system kill 9 7508 #terminate the process rm filename # delete mkdir
-
linux more vs less?
- more: forward navigation and limited backward navigation
- less: both forward and backbackward naviation and search options.
- with less, can go start and end of file
- less is better for large input files it starts up faster than text editors like vi.
-
Why Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Protocol is used?
- ICMP used to communicate problems in network communicate problems with data transmission
- eco request and eco reply
- Firewall rules for ICMP (TCP/UDP port 7)
- DevOps Deployment strategies?
- Recreate: Version A is terminated then version B is rolled out.
- Rolling-update/incremental: Version B is slowly rolled out and replacing version A.
- Blue/Green: Version B is released alongside version A, then the traffic is switched to version B.
- Canary: Version B is released to a subset of users, then proceed to a full rollout.
- A/B testing: Version B is released to a subset of users under specific condition.
- Shadow: Version B receives real-world traffic alongside version A and doesn’t impact the response.
- How you perform Hot deployment in Cloud?
- using Canary
- Explain Biggest issue in PROD ?
- How you scale prod ?
- DevOps vs Agile
- Rollback Strategy for Canary?
-
Diff between git pull and git clone
- pull is remote branch changes will be added locally & commit
- fetch is fetches but not commit
-
How to delete previous commit from pushed repo
- git reset --hard
-
Diff between git merge and git rebase
- merge combines source branch to a target branch, preserves the entire history
- rebase overwrites the changes
-
Diff between git pull vs git fetch
- git fetch retrieve the latest meta-data from original
- git pull brings the changes from remote & adds in local but not commit
-
git clone specific branch
- git clone -b brnachname
-
git stash
- temparary save
-
git how to revert specific branch
- git log (Shows the commit logs)
- git revert commitID (directly commits/reverts )
- git revert -n commitID (merges the changes but not commit)
- git reset --hard commitID (resets & reverts the changes)
-
git differnece
- git diff (Shows the changes between unstaged files and the commits)
- git diff --staged (Shows the changes between staged(ready-to-be-committed) files and the commits)
-
git find list of commited files
- git log --oneline
- What is default docker network applies when creating containers
- default bridge network are usually used when your apps run in standalone containers that need to communicate]
- Explain Container Network Model?
- Network Controller - Provides the entry point into libnetwork
- Driver - Provides actual implementation that makes n/w work
- Network - Is an implementation of CNM: Network
- End Point - Provides the connectivity for services exposed by container in n/w
- Sandbox - represent container's n/w configuration (IPaddr,MacAddr,routes,dns etc)
- Docker Network Drivers ?
- Bridge - default n/w driver to communicate sandalone containers
- Host - uses host networking directly, cannot run same containers on same port
- None - disables n/w for containers
- Overlay - connects multiple docker daemons together and enable docker daemons to communicate each other
- Mcvlan - allows to assign MacAddress so that it will appear as physical device. useful for legacy apps
- IPvlan - total control over both IPv4 and IPv6, network integration of IPvlan L2 & L3
- none -
- How docker resolves the container names ?
- docker has builtin dns server in Sandbox which help containers to resolve IP using its name
- docker creates network namespaces to isloate
- What is docker compose ?
- utility to define multiple containers as YAML in declarative way
- Diff between docker CMD and ENTRYPOINT ?
- CMD defines default commands and/or parameters for a container
- ENTRYPOINT is preferred when you want to define a container with a specific executable
- Combine ENTRYPOINT with CMD if you need a container with a specified executable and a default parameter that can be modified easily
- How can we make docker image lightweight ?
- using multi stage builds
- How docker builds images?
- using layers, layers 1 base image, layer 2 run app packages, layer 3 copy files...
- docker re-use layers from cache
- How many types of docker volume mounts?
- volume mounting - mount from volume location
- docker run --mount type=volume, source=/var/lib/mysql,target=/var/lib/mysql mysql
- bind mounting - mount from any location - /data/mysql:/var/lib/mysql
- docker run --mount type=bind, source=/data/mysql,target=/var/lib/mysql mysql
- volume mounting - mount from volume location
- What is the Branching Strategy to you use
- How you will fix prod issues
- What is the end to end flow of CI CD
- Explain CI
- Explain Continuous Delivery and Continuous deployment
- Delivery automating the entire software release process
- Delivery everthing is auto but has manual step before deploying in PRD
- Deployment is a step up from Continuous Delivery
- Deployment evey step is auto
- Where to store artifacts
- How you used Ansible in your project
- Archtecture of Ansible
- What are ansible facts?
- Diff between Ansible & Terraform
- What are the Ansible roles
- What are the Ansbile valuts
- if inventory is dyanmic
- How to enable detailed logs
- Ansible tower
- Dynamic Inventory
- Ansible how you avoid prompt
- ansible copy
- Ansible vs chef vs puppet
- How do you store secrets in terraform
- store in AWS Secret manager
- read from TF code using aws_secretsmanager_secret_version
- using TF locals jsondecode and give reference
- What is local & remote provisioner
- local exec executes code on the machine running terraform
- runs on the provisioned resource
- What are the terraform modules, explain an an example
- code reuse, versioning, support remote storage
- Where the terraform logs are stored
- TF_LOG to JSON outputs logs at the TRACE level
- $ export TF_LOG="TRACE"
- TF_LOG_PATH for persistent log path
- $ export TF_LOG_PATH="terraform.txt"
- TF_LOG to JSON outputs logs at the TRACE level
- How to rollback terraform if error occurs?
-
Explain kubernetes architecture ?
-
If i give 3 servers, how you setup kubernetes ?
-
kubernetes diff components ?
- master, controller, scheduler, ETCD, flannel & caliko
- node, container run time, kubelet, kubeproxy
-
What are the taints & tolerations ?
- Taint will be applied to nodes as key value paid, will allow to force set of pods
- Tolerations will be applied to pods, allow the pods to schedule onto nodes with matching taints.
-
Assigning Pods to Nodes - Node Affinity
- nodeSelector is a field of PodSpec
- Node affinity (under pod spec) is similar to nodeSelector but more expressive syntax
- requiredDuringSchedulingRequiredDuringExecution. it allows you to constrain which nodes your pod is eligible to be scheduled on, based on labels on the node
-
How you acheive pod security
- use securityContext in pods runAsUser, runAsGroup, runAsNonRoot & fsGroup
- use securityContext => linux capabilities
-
Explain about Stateful sets
- like deployment but maintains a sticky identity for each Pods, not interchangeable & persistent identifier
- must need pv, headless service
- Stable, unique network identifiers
- Stable, persistent storage
- Ordered, graceful deployment and scaling
- Ordered, Automated rolling updates
-
Headless service
- used for Statefiul set pod
- No Load balancing, directly interact with Pod
- service discovery with service name
-
What is Init container
- Specialized containers that run before app containers in a Pod
- used for setup scripts
-
Diff between deployment, service and daemonset
- Deployments manage stateless services
- DaemonSets attempt to adhere to a one-Pod-per-node model
- Service is an abstract way to expose an app running on a set of Pods as a network service
-
Explain kubernetes reverse proxy
- Ingress exposes HTTP and HTTPS routes from outside the cluster to services within the cluster
- Ingress maps service
- http path based
-
Proxies in Kubernetes
- kubectl proxy
- apiserver proxy
- kube proxy
-
k8s create vs apply
- imperative
- declarative
-
k8s pod life cycle
-
k8s startup probe liveness & ready probe
-
k8s High avail:
- liveness & readyness probe
- HoriPodAutoscaler VirtualPodAutoscaler
- network policies
- use volumes for stateful & helper
-
k8s namespaces in default installation
- dafault
- kubesystem
- kubepublic
- kubenoderlease
-
why we attach resource quota. create resource quota for namespace
-
k8s sidecar containers
-
K8s volume types
-
k8s adapter containers
-
k8s network policy
- ingress & egress
- ipBlock
- namespaceSelector
- podSelector
- ports
-
K8s pod disruption budget
- volunatry and non voluntary... in case of any down... minimum 1 should be there
-
k8s operators or custom resource definitions
- in case of stateful applications
-
k8s control loop mechanism
- default mechanism... observe and take action on
-
Helm3
- no tiller, 3-way-verification, schema verification, release namespace.
-
use of networking solutions calico/flannel
- 4 nodes
- make sure unique IP's created
-
use of PV & PVC (local & remote storge)
- volumes
- PV use central volume like EFS/EBS
- PVClaim - attach to pod
-
which one is default deployment strategy? how it works?
-
command to check the container logs in pod?
-
what are the types of services present in kubernetes?
-
What is the link between pod and service?
- How you Host DB if DB has to be in the region where AWS/AZURE not avail
- Diff between Stateful and Stateless firewalls ?
- Cloud Formation, how you will solve circular dependency issue ?
- How you will setup to find uptime in AWS?
- How to monitor a website in AWS ?
- How to maintain AutoScalingGroup old instance logs ?
- Explain DNS resolution in Route53 ?
- Data security point of view what are options you will choose in AWS ?
- Authentication mechanism in GCP ?
- What is the complete workflow in DevSecOps process?
- What is SAST ?
- What is DAST?
- What you monitor in Sonarqube
- What is the benefit of Fortify ?
- What you monitor in Sonarqube ?
- How you deal Cross site scripting ?
- What is SQL Injection?
- How do you secure git repo ?
- How do you secure pipeline?
- How do you check docker image for volunarables?
- Network level security?
- Load Testing?
- Stress Testing?
- What libraries you have used in python
- List comprehension
- Decorators/Iterator/Generators
- OOPS
- Slicing concept
- List vs Tuple
- How list are implemented in python?
- Hashing[Collision]
- self and new method difference in python
- Lambda function in python
- Deep and shallow copy
- pop() and remove() difference
- Global and local variable and nonlocal in python